Bacteria Organize According to 'Rich-Get-Richer' Principle
Research could help in battle against infections that do not respond to powerful drugs
Bacteria on a surface wander around and often organize into highly resilient communities known as biofilms. It turns out that they organize in a rich-get-richer pattern similar to the distribution of wealth in the U.S. economy, according to a new study by researchers at UCLA, Northwestern University and the University of Washington.
The study, published online May 8 in the journal Nature, is the first to identify the strategy by which bacteria form the microcolonies that become biofilms, which can cause lethal infections. The research may have significant implications for battling stubborn bacterial infections that do not respond to antibiotics.
 Bacteria in biofilms behave very differently from free-swimming bacteria. Within biofilms, bacteria change their gene expression patterns and are far more resistant to antibiotics and the body's immune defenses than individual, free-swimming bacteria because they mass together and are protected by a matrix of proteins, DNA and long chain-like sugar molecules called polysaccharides. This makes seemingly routine infections potentially deadly.
Bacteria in biofilms behave very differently from free-swimming bacteria. Within biofilms, bacteria change their gene expression patterns and are far more resistant to antibiotics and the body's immune defenses than individual, free-swimming bacteria because they mass together and are protected by a matrix of proteins, DNA and long chain-like sugar molecules called polysaccharides. This makes seemingly routine infections potentially deadly.
Gerard Wong, a professor of bioengineering at the UCLA Henry Samueli School of Engineering and Applied Science, a member of the California NanoSystems Institute and a professor of chemistry and biochemstry at UCLA; Erik Luijten, an associate professor of applied mathematics and of materials science and engineering at Northwestern University’s McCormick School of Engineering and Applied Science; and Matthew R. Parsek, a professor of microbiology at the University of Washington, led a team of researchers who elucidated the early formation of biofilms by developing algorithms that describe the movements of the different strains of the bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa and by conducting computer simulations to map the bacteria's movements. P. aeruginosa can cause lethal, difficult-to-treat infections, including those found in cystic fibrosis and AIDS patients.
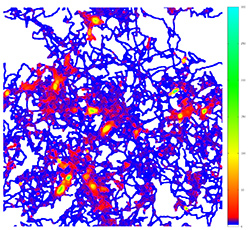
Surprisingly, the researchers found that the individual bacteria that start the formation of microcolonies have no special, inherent qualities. As bacteria move across a surface, they leave trails composed of a specific type of polysaccharide called Psl.
“Some of the bacteria remained fixed in position,” Parsek said. “But some moved around on the surface, apparently randomly, but leaving a trail that influenced the surface behavior of other bacteria that encountered it.”
 Bacteria arriving later also lay trails, but their movements tend to be guided by the trails from the pioneers. This network of trails creates a process of positive feedback and enables bacteria to organize into microcolonies that mature into biofilms. By being at the right place at the right time, and by using communally produced polysaccharides, a small number of lucky cells -- often ones that come later -- become the first to form microcolonies. Cells in microcolonies have many survival advantages over other bacteria.
Bacteria arriving later also lay trails, but their movements tend to be guided by the trails from the pioneers. This network of trails creates a process of positive feedback and enables bacteria to organize into microcolonies that mature into biofilms. By being at the right place at the right time, and by using communally produced polysaccharides, a small number of lucky cells -- often ones that come later -- become the first to form microcolonies. Cells in microcolonies have many survival advantages over other bacteria.
Interestingly, the researchers found that these biofilms develop in accordance with Zipf's Law, which has been used to describe the rich-get-richer phenomenon. A well-known example of this is the distribution of wealth in the United States. The wealthiest 20 percent of the population owns more than 80 percent of the total wealth. Most of the wealth in this elite group, in turn, is owned by a small fraction of that elite. This pattern of ownership repeats for higher levels of wealth.
“It turns out bacteria do something similar,” Wong said. “A small number of bacteria have the best access to the lion’s share of communally produced polysaccharides.”
Wong said the research may provide insight into how to fight antibiotic-resistant bacteria.
“Typically, when we want to get rid of bacteria, we just kill them with antibiotics,” he said. “As a result, they develop defense mechanisms and grow stronger. Maybe that's not always the best way to treat biofilms. Perhaps we can regulate bacterial communities the way we regulate economies. Our work suggests that new treatment options may use incentives and communications as well as punishment to control bacterial communities.”
Luijten said that the group's findings were possible because the researchers drew knowledge from their various individual disciplines. “Only through combination of the totally different types of expertise of three different research groups has it been possible to disentangle what is going on and how polysaccharides influence the organization of bacteria into microcolonies,” he said.
The paper, “Psl trails guide exploration and microcolony formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms,” is available online.
Postdoctoral researchers Kun Zhao of UCLA's department of bioengineering and Boo Shan Tseng of the University of Washington are the paper's lead authors. The principal investigators are Wong, Parsek and Luijten. Other authors include Joe Harrison of the University of Washington, Professor Fan Jin of the University of Science and Technology of China in Hefei, Northwestern University graduate student Bernard Beckerman and UCLA graduate student Maxsim Gibiansky.
The research was supported by the National Institutes of Health, the National Science Foundation, the Cystic Fibrosis Foundation, the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada and a UCLA Transdisciplinary Research Grant.