A Faster Internet for Your Smartphones
The freedom to choose the best DNS for your phone and carrier can change your mobile web experience.
Most of us spend a significant portion of our time on our phones. So when the Internet connection slows or stalls, it can interrupt our lives to a maddening degree. We complain about the network, shut down apps, and double-check our bars to troubleshoot the problem. But a Northwestern research team recently found that an unexpected culprit lurking in the background might be what’s to blame.
Domain Name Service (DNS) is a critical piece of infrastructure within the Internet. To visit a website or use an application, we employ their names, such as www.facebook.com or www.northwestern.edu, as though these were their addresses in the Internet. The truth is a bit more complicated. The site’s address in the Internet is actually a string of numbers, which tend to be difficult for us to remember. Making our lives easier, DNS sits behind the scenes, translating every user-friendly name to the correct Internet address. Every time we visit a website, chat with friends, or send an email, we rely on DNS. Not surprisingly, a badly performing DNS can greatly impact the mobile experience.
 “At first we wondered if DNS had an impact on performance,” says Fabián Bustamante, associate professor of electrical engineering and computer science at the McCormick School of Engineering and Applied Science. “Does it matter? It turns out that it matters a lot.”
“At first we wondered if DNS had an impact on performance,” says Fabián Bustamante, associate professor of electrical engineering and computer science at the McCormick School of Engineering and Applied Science. “Does it matter? It turns out that it matters a lot.”
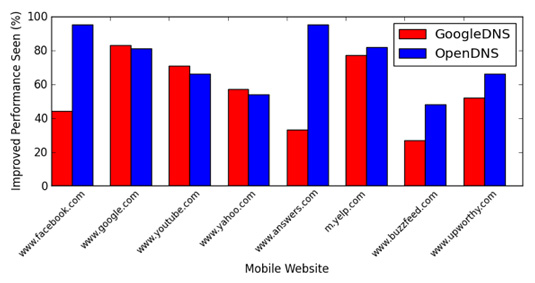
Along John Rula, fourth-year PhD candidate, Bustamante launched a new mobile application called Namehelp Mobile, to explore this question. The app allows users to measure DNS performance provided by their companies and compare it with public DNS systems, such as GoogleDNS or OpenDNS. The team found that by simply choosing the “right” DNS for them, users could improve their web performance by up to 150 percent.
Namehelp Mobile allows users to learn the best DNS choices wherever they are and whatever their carrier. The application is now available for Android phones at the Google Play Store. Bustamante and Rula hope that, eventually, cellular phone carriers will stop limiting DNS options and give their customers the freedom to choose.Cell phone carriers, however, lock down DNS service options on their devices, limiting consumer choice. “Because consumers are locked into their DNS service,” Rula says, “they don’t know what they are missing.” Currently, the only option to bypass this limitation is a rooted or “jailbroken” phone.
This project is one of many in Bustamante’s AquaLab group, where they explore the challenges and opportunities of the ever-growing Internet with an experimental approach, focused on the design, deployment, and evaluation of systems that people use.